
OTC FX Trading Value in Japan was Over 10 Quadrillion for 2 Consecutive Years
Jan. 30, 2024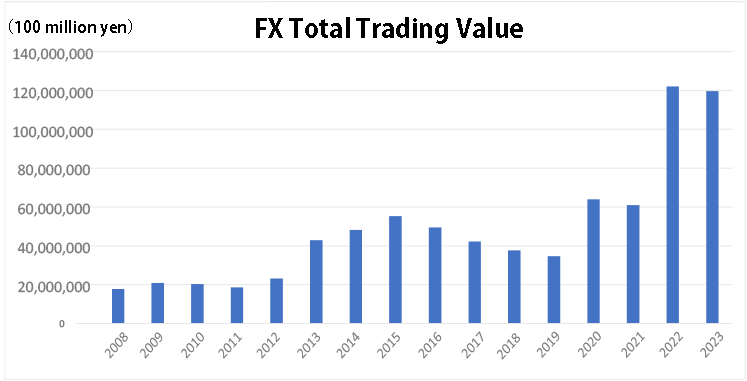
The trading value in 2023 by individual traders at OTC(Over-The-Counter) FX member traders in Japan was less than 10 quadrillion 2,000 trillion yen, slightly less than it in 2022, but keeping the high level, following on from 2022 when it exceeded 10 quadrillion yen for the first time.(The changes of past trading value are posted below)
Individual investors trading against the trend to the ongoing depreciation of yen seems to have become more active, so trading value share of USD/JPY currency pair was 84 percent in all currency pairs, hitting an all-time high, up from 75 percent in 2022.
According to the monthly OTC FX preliminary report announced by the Financial Futures Trading Association of Japan on January 18, the trading value at 47 OTC FX member traders in December last year was 1,209,309,700,000,000 yen (22.0 percent up compared to the previous month, 22.1 percent up year on year).
FX was born in April 1998 in Japan and the reason for its birth was liberalization of exchange in principle due to a fundamental revision of Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Act. It was so-called “Japanese version of financial big bang”, and until then, specified financial institutions were the only ones authorized to conduct foreign exchange operations, however, since it opened to the public, it is possible to conduct FX trading.
In the beginning of 2000s, although some rapacious FX traders repeatedly caused social troubles such as forceful solicitation, the amendment of Financial Futures Trading Act was enforced in July 2005 and FX traders were required to register, and after that, its business system gradually improved.
In October 2007 when Financial Instruments and Exchange Act was enforced, Financial Futures Trading Act (the old act) was integrated into Financial Instruments and Exchange Act, which aimed for “User protection in trading financial products with investment properties, and creating a transparent and fair market”.
In August 2010, Cabinet Office Ordinance to amend part of Cabinet Office Ordinance concerning Financial Instruments Business, etc. was enforced and transitional measures to set margin rate at 2 percent were established, that was the 50x leverage limit.
In August 2011, rules for margin rate to be 4 percent or more―the 25x leverage limit―were established. As these market modification measures were overlapped, soundness in FX business management improved. However, traders that judged FX business wasn’t very profitable withdrew from the business. So after that, the number of FX traders followed a decreasing trend.
After that, this situation led to a concentration of transactions among the top few traders, and as a result, some point out that raising the hurdles for new traders to enter so far. Commodity futures traders have been actively engaged in FX business since its inception and 6 commodity futures traders continue to handle “Click 365”, currently the only exchange FX transaction on Tokyo Financial Exchange as before.
(Futures Tribune・issued January 23, 2024 ・no.3264)
Link(Japanese site)
©2022 Keizai Express Corp.